Converting a string into a Pandas df
Rationale
Standard ways to construct a Pandas dataframe from data (e.g., from a dict or a list of lists) are extremely cumbersome, especially for longer dataframes with many rows. Our goal is to introduce a tool that allows to create a Pandas dataframe from its string representation, which is much more readable.
Compare the data needed to create a df in a standard way:
data = {
1030828978: [0.20136, 0.20158, 0.20162, 0.20128, 0.20134, 0.20110],
1464553467: [
1838.812,
1839.690,
1839.936,
1839.430,
1840.016,
1839.615,
]
}
timestamps = pd.date_range(
start="2023-08-15 11:45:00",
end="2023-08-15 12:10:00",
tz="America/New_York",
freq="5T",
)
To the data needed to create a df with our tool:
df_as_str = """
1030828978 1464553467
end_timestamp
"2023-08-15 11:45:00-04:00" 0.20136 1838.812
"2023-08-15 11:50:00-04:00" 0.20158 1839.690
"2023-08-15 11:55:00-04:00" 0.20162 1839.936
"2023-08-15 12:00:00-04:00" 0.20128 1839.430
"2023-08-15 12:05:00-04:00" 0.20134 1840.016
"2023-08-15 12:10:00-04:00" 0.20110 1839.615"""
How to use
- The function is
str_to_df(), located inhelpers/hpandas.py - To use the function, one needs to provide a string representation of the df and the mappings between the columns and the desired types of column names and values
- For example, given the string representation of a df in the previous section and the following mappings:
col_to_type = {
"__index__": pd.Timestamp,
"1030828978": float,
"1464553467": float,
}
col_to_name_type = {
"1030828978": int,
"1464553467": int,
}
str_to_df() will output the following dataframe:
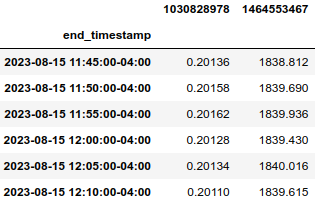
- More usage examples can be found, e.g.:
- In the dedicated unit tests in
helpers/test/test_hpandas.py::Test_str_to_df - In practical use cases in
oms/order/test/test_order_converter.py
Notes
- The string representation used as an input to the function should be largely
the same as the output of
hpandas.df_to_str(). Note that it is not the same as the output ofstr(), which is much less controlled and therefore messier than ofdf_to_str()(e.g., the column names are often split into different rows far away from each other, etc) - There are several differences between the raw output of
df_to_str()and the required format of the input tostr_to_df(): - If the number of rows is over a certain number, then
df_to_str()cuts them, leaving only the head and the tail of the df, and everything in between is replaced by the "[...]" placeholder. Instr_to_df(), the placeholder "[...]" is simply removed and the data it stands for cannot be restored - In the input to
str_to_df(), values that contain spaces (e.g., a timestamp like "2000-01-01 09:00:00") need to be enclosed in double quotation marks. If there are values with spaces in the input todf_to_str(), then it will convert them into strings but will not automatically put quotation marks around them, which means that if we attempt to convert the output string back into a df withstr_to_df()without adding the quotation marks manually, these values will be split into two different columns, possibly also breaking the whole process due to the column number mismatch